Project Cost Estimating: How to Accurately Do It Every Time
Table of Contents
It’s a natural thing for people to look forward to the future. Whether it’s planning a trip, preparing for the weather, or budgeting for the next fiscal year, we’re constantly learning how to estimate for upcoming events. But, unlike misreading the weather or picking a subpar hotel, mistakes in project cost estimation have serious implications for the success of a project — not to mention the impact on a company’s bottom line.
In the business world, project management, finance, and operations leaders have the difficult job of balancing budgets with the quality and scope of a project. Proper cost estimation is crucial to achieving this balance and keeping companies in the black.
What is Project Cost Estimation?
Cost estimation is the process of forecasting the financial and resource investment necessary to complete a project within its defined scope.
From the requisite materials to direct labor and administrative overhead, each project element is used in the cost estimation process to determine its budget.
Project cost estimations can be preliminary estimates that help companies decide whether or not they wish to pursue a project or a resource that informs what the final scope of the project will be.
What Goes Into Cost Estimation?
To properly estimate project cost, project management, finance, and operations leaders must run through a series of steps that tie high-level project goals to the financial reality of carrying it out. These steps include:
- Completely defining the project
- Creating a timeline
- Adopting a billing structure
- Selecting a project estimation method (bottom-up, parametric, etc.)
To estimate the cost of any project accurately, you must understand the two main types of cost incurred throughout any project: Direct and indirect.
Direct costs
Direct costs are the costs of a project that are directly connected to a cost object, such as a specific product, project, or department. Common examples of direct costs include:
Direct Labor: The cost of team members working on the project, both in terms of wages and time
Direct Materials: The cost of physical and digital resources required for the project
Commissions: The cost of paying sales representatives for the completion of a sale
Direct costs are typically variable in nature as they fluctuate along with the cost of production. For example, the direct costs of building a condo include building materials, skilled labor, and subcontractors.
Indirect costs
Indirect costs don’t fit neatly within one specific cost object and are incurred by the organization at large. Indirect costs are typically those that allow companies to maintain and operate, including:
Office and Retail Space: The cost of using any working spaces not owned by the organization
Utilities and Overhead: The cost of running and maintaining a facility or workspace
Administrative Salaries: The cost of employing administrative personnel
Because these costs don’t vary alongside production costs, indirect costs are typically fixed or semi-variable. For that same condo construction project, the indirect costs might include a mobile office, equipment repairs, and quality control of the building material.
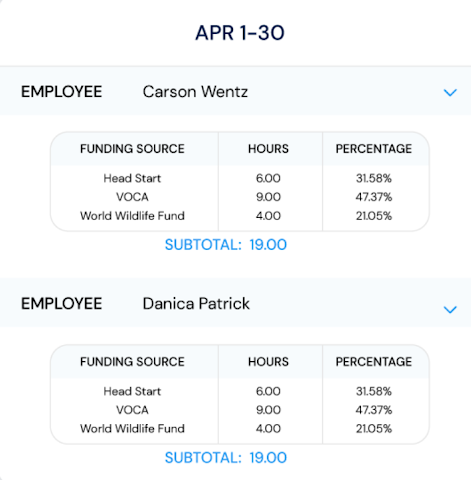
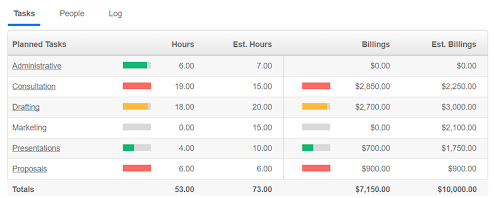
Track Direct and Indirect CostsProject Costing
See profit margins, direct labor hours,
and projected billing total for any project.
See your projects’ real costs
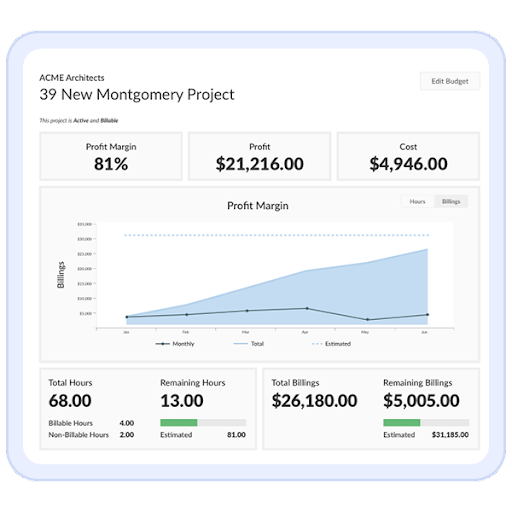
How To Accurately Estimate Project Costs
The goal for any project, finance, or operations lead going into a new project is for the estimated cost to align with the actual cost.
Getting your budget as close to the real cost as possible is difficult but not impossible. Here are some keys to accurately estimating project cost:
- Identify tasks and work needed to be done
- Develop a timeline for task completion
- Allocate resources to complete the work
- Calculate cost based on resources & timelines
- Note any risks that may disrupt the project
- Monitor progress with a tracking platform built for project accounting
What Makes a Good Cost Estimate?
A good cost estimate precisely and reliably projects how much a project will cost. Typically, this means that the project manager has taken a thorough, accurate appraisal of all related costs, timelines, and potential risks.
Common Project Estimation Mistakes
While this may seem like a straightforward process, businesses make plenty of common project estimate mistakes when they get into the nitty-gritty. For instance:
- Basing timeline estimates off previous, poorly-managed projects
- Lack of experience estimating for similar projects
- Incomplete view of the project scope
- Misalignment on true resource productivity
- Letting internal pressure distort estimates
For new managers who lack experience with the fundamentals of cost analysis, running over budget is an all-too-common problem — one affecting projects across many industries. In many cases, the problem actually starts before the project even begins because cost estimates are plagued by these common mistakes.
Commonly Used Tools for Cost Estimating
Cost estimation is commonly conducted using spreadsheets that allow project managers to input and organize data and perform calculations. But businesses are increasingly using more powerful platforms to improve the accuracy of these projects. Some of the most common tools for cost estimating include:
- Excel
- Google Sheets
- ERP Systems (Enterprise Resource Planning)
- ClickTime
While Excel and Sheets are useful for estimating the cost of smaller projects, they are more time intensive and difficult to use.
Software platforms like ClickTime empower project, operations, and finance managers with additional features like access to historical project cost data, configurable employee cost rates, and capacity planning tools.
Make Accurate and Reliable Project Cost Estimates with ClickTime
As a powerful time-tracking software, ClickTime empowers business leaders to create cost estimates that align with the project’s real cost.
Use ClickTime to get your projects off the ground and stay on budget!